Rules of application is are. This rebellious verb to be...How to make friends with a child? Interesting and useful exercises for children
Hello my dear.
Today I come to your aid in the fight against a frequent guest English sentences: verb to be. Don't be afraid, he's not as scary as he seems. Therefore, arm yourself with knowledge and practice ahead, because you have a minimum of theory and a maximum of practice ahead of you.
Then I officially start the lesson called: verb to be - exercises for children.
Few rules
Verb to be translated means “to be.” And it is used in almost EVERY sentence of the English language. How? - you ask. - What about the sentences “I’m beautiful”, “I’m a schoolboy”, “Are you at home?”, “I’m in class”? The answer is simple: in English language this verb is helped by 3 little friends who, in Russian, simply remain invisible. These are verbs am, is, are.
You can remember the use of the verbs am, is, are using the example of your family. If we talk about ourselves beloved, then we use the form am . If a sister, brother, or even a cat lives with you, then you can talk about each of them is . But we need to talk about parents together are .
See:
Exercises
Let's practice verb forms. If your child has entered 1st grade, then the most important thing for him now is to remember which form is used with which pronoun.
Exercise 1:
Insert the correct form of the verb to be: am, is, are.
1. I _____ a girl.
2. He ____ my brother.
3. She ____ my sister.
4. I ____ from London.
5. He ____ 17 years old.
6. She ___ a student.
7. They ____ our parents.
8. We ____ a family.
9. It ____ our dog.
10. You ____ our friend.
Once in 2nd grade, he lexicon will be much larger and he can already put forms of verbs without the presence of explicit pronouns.
Exercise 2:
My name (1) ____ Kate Rusak. I (2) ___ 12 years old and I (3) ____a student. My family (4) ____ from Moscow. My address (5) ____ Pushkina str., 9. My telephone number (6) ____ 345 78 54. I have a sister and a brother. Their names (7) ____ Pasha and Valya. Pasha (8) ____ 17 years old. He (9) ____ a sportsman. His team (10) ____ the winner of the local championship. Valya (11) ____ 7 years old. Her school (12) ____ not far from our home.
Our parents (13) ____ busy. My mother (14) ____ a doctor and my father (15) ____ a lawyer. We (16) ___ a very happy family. We spend every weekend together.

If your child has already entered 3rd grade, then he simply needs to understand how the negative form of verbs is formed. Here's how it happens:

Let's practice.
Exercise 3:
Write a sentence with contracted and negative forms of verbs.
1. We are a big family.
2. He is a good student.
3. He is a swimmer.
4. My parents are doctors, and my aunt is a teacher.
5. You are a nice person.
6. It is a beautiful picture. We are happy to have it.
7. I am good at writing, and my sister is good at drawing.
8. She is a singer. Her song is very beautiful.
9. It is cold today. We are going to school on the bus.
10. They are very happy. They have a big family.
Exercise 4:
Select correct option. Translate into Russian.
1. They aren’t/aren’t doctors. They are/is teachers.
2. I am/is a student. I go to school by bus. The bus stop is/are not far from our home.
3. I am/is sure that you are/are wrong. They are not/is not liars.
4. She is/is proud of you. You are/are a worker.
5. It is/am getting cold. You sweater are/is in your backpack.
Well, if your child is already quite an adult and has entered the 4th grade, or even better, the 5th grade, then feel free to give it to him collection of exercises on English grammar for children . I'm sure he can handle this quite well. And I have one more exercise for you.
Exercise 5:
Translate the text into English.
My name is Kirill. I am 10 years old and a schoolboy. I'm in 4th grade. I have big family. My mother is a doctor. She's in the hospital now. My dad is not a doctor. My dad is an athlete. He's in training now. I have 2 grandmothers and 2 grandfathers. They are now in the village. We live in Moscow. Our address: st. Kostromskaya, 18, apt. 76. Our phone number is 8 800 342 23 76. I have a sister. Her name is Marina. She is 15 years old. She is also a schoolgirl. She loves to read and draw. Her paintings are very beautiful.
We have many animals at home. This is our cat. Her name is Valya. This is our parrot. His name is Kesha. This is our dog. Her name is Barney.
We are all a big and friendly family.
goodbye
Do you remember what the key to successful learning is? The point is to have interest. It doesn't matter whether you're looking for exercises for beginners or for professionals, or for adults - make it interesting. Practice, look for interesting exercises, look for interesting forms and methods of teaching, and then this process will become easy and fun.
One of these auxiliary, fascinating and at the same time very effective methods learning is online service lingualeo(read about it in more detail in) . I can say that everything is thought out there in such a way that the child himself will strive to learn English. Try it and see for yourself. Registration and a huge amount of materials are free.
And if there is something you don’t understand, then ask your questions in the comments! I will be happy to help you on this path of learning English.
Answers.
Exercise 1:
1. I am a girl.
2. He is my brother.
3. She is my sister.
4. I am from London.
5. He is 17 years old.
6. She is a student.
7. They are our parents.
8. We are a family.
9. It is our dog.
10. You are our friend.Exercise 2:
My name (1) is Kate Rusak. I (2) am 12 years old and I (3) am a student. My family (4) is from Moscow. My address (5) is Pushkina str., 9. My telephone number (6) is 345 78 54. I have a sister and a brother. Their names (7) are Pasha and Valya. Pasha (8) is 17 years old. He (9) is a sportsmen. His team (10) is the winner of the local championship. Valya (11) is 7 years old. Her school (12) is not far from our home.
Our parents (13) are busy. My mother (14) is a doctor and my father (15) is a lawyer. We (16) are a very happy family. We spend every weekend together.Exercise 3:
1. We are a big family. - We're a big family. - We are not (aren’t) a big family.
2. He is a good student. - He’s a good student. - He is not (isn’t) a good student.
3. He is a swimmer. - He’s a good swimmer. - He is not (isn’t) a swimmer.
4. My parents are doctors, and my aunt is a teacher. - My parents are doctors, and my aunt’s a teacher. - My parents are not (aren’t) doctors, and my aunt is not (isn’t) a teacher.
5. You are a nice person. - You’re a very nice person. - You are not (aren’t) a very nice person.
6. It is a beautiful picture. We are happy to have it. - It’s a beautiful picture. We're happy to have it. - It is not (isn’t) a beautiful picture. We are not (aren’t) happy to have it.
7. I am good at writing, and my sister is good at drawing. - I’m good at writing, and my sister’s good at drawing. - I am not good at writing, and my sister is not (isn’t) good at drawing
8. She is a singer. Her song is very beautiful. - She’s a singer. Her song's very beautiful. - She is not (isn’t) a singer. Her song is not (isn’t) very beautiful.
9. It is cold today. We are going to school on the bus. - It’s cold today. We're going to school on the bus. - It is not (isn’t) cold today. We are not (aren’t) going to school on the bus.
10. They are very happy. They have a big family. - They’re very happy. They have a big family. - They are not (aren’t) very happy. They don't have a big family.Exercise 4:
1. They aren’t doctors. They are teachers.
2. I am a student. I go to school by bus. The bus stop is not far from our home.
3. I am sure that you are wrong. They are not liars.
4. She is proud of you. You are a worker.
5. It is getting cold. You sweater is in your backpack.Exercise 5:
My name is Kirill. I am 10 years old and I am a pupil. I am in the 4th form. I have a big family. My mother is a doctor. She is at the hospital now. My father is not a doctor. My father is a sportsman. He is at the training now. I have 2 grandmothers and 2 grandfathers. They are in the village. We live in Moscow. Our address is: Kostromskaya str, 18, ap. 76. Our telephone number is 8 800 342 23 76.
I have a sister. Her name is Marina. She is 15. She is a pupil too. She likes to read and to draw. Her pictures are very beautiful.
We have a lot of animals at home. It is our cat. Her name is Valya, It is our parrot. His name is Kesha. It is our dog. His name is Barni.
We are a big and friendly family.
It is with this verb that you need to start studying English grammar. Verbs in English do not change for persons, but the verb to be is an exception. Using this verb, we will learn to compose simple sentences that do not contain a verb in Russian, for example, “I am a student,” “he is at home,” “this is interesting,” etc. In English it is unacceptable to form without a verb that performs the action, and to be serves as a linking verb. For example, to say “I am a student,” we must insert the desired form of the linking verb to be and, as a result, the sentence will take on the meaning “I am a student” - “I (am) a student.”
Forms of the verb to be in the present tense
In the present tense, the verb to be has three forms: AM, IS, ARE:
- Remember: to be and AM, IS, ARE are not 4 different ones, but forms the same verb:
Google shortcode

(We hope our dragon will help you remember this)
Let's look at how the verb to be changes in the present tense
Affirmative form
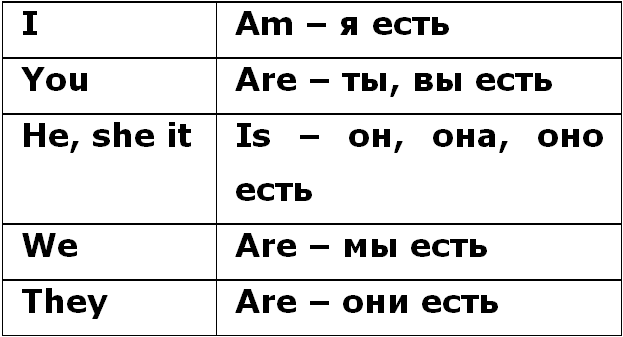
- We are friends - we are friends
- They are busy - they are busy
- The book is thick - the book is thick
- It is a cat
- She is clever - she is smart
Negative form

To form a negative conjugation form of a given verb, you need to put a negative particle “not” after one of required forms verb (am, is or are). Here are some examples of negative sentences:
- I am not hungry – I am not hungry
- He is not busy
- The room is not big – the room is not big
Interrogative form

To form an interrogative form, you need to put the appropriate form of the verb (am, is or are) at the beginning of the sentence:
- Are you Peter? -Are you Pete?
- This room? – Is this a room?
- Are you hungry? -Are you hungry?
- He is busy? – Is he busy?
- To understand how verbs live in the English language, let’s first remember at least one Russian verb in its initial form, for example, the verb “to live”. As you know, Russian verbs in their initial form end in “-т”, and later, when conjugated, the ending changes. As for the English language, the verb in its initial form is used together with the particle to, for example, we say to be – would t, find t Xia, i.e. if the particle to precedes the verb, this means that the verb is in the initial form, and when further using the verb with persons, this particle is omitted. Let's give an example: “To be or not to be” - there are two verbs in the sentence - and both are in the initial form, and they must be used together with the particle to, and, accordingly, we will translate into English as “to be or not to be”. If we have before us the sentence “I (am) a student,” i.e. we have changed the verb according to the person of the subject, then the particle to is omitted and the proper form of the verb is used, in in this case- am.
- Unlike the verb to be, other verbs in English are not conjugated, for example, the verbs “live, sit, love” in the initial form are translated into English “to live, to sit, to love”, i.e. with a particle to, and when conjugated - without to, for example, “I live, sit, love” will be translated into English as “I live, sit, love,” i.e. initial form of a verb in English without a particletonot used, but when conjugatedtofalls. Initial form in English it is called Infinitive - Infinitive.
More about the particle to watch our video tutorial:
Verb conjugations tobe in present time
Now let's learn how the verb to be changes (conjugates) in the present tense. As mentioned above, in Russian, sentences like “I am a student, she is a doctor, we are workers” are formed without a predicate verb. But to translate these sentences into English, you need to put the appropriate form to be after the subject - “I am a pupil, she is a doctor, we are workers.”
Please note the translation of the following sentences in affirmative, negative and interrogative forms into English:

Verb conjugations tobe in past and future tense
In the past tense, the verb to be has two forms - was and were (was, was, were)

In the future tense, the verb to be is conjugated as follows

Note: In modern English the form shall is rarely used to form the future tense of verbs (although its use is not a grammatical error), the form is used for all persons will. Therefore, sometimes there are discrepancies in different textbooks.
To summarize, consider the following table:

Here are some commonly used verb expressions: to be which you should learn and conjugate yourself using the conjugation table:
- To be happy/unhappy – to be happy/unhappy
- To be glad - to be joyful
- To be hungry/to be full up– to be hungry/full
- To be fond of - to love, be carried away by something
- To be busy - to be busy
- To be late (for) - to be late (for)
- To be in time for - to be on time
- To be present at – to be present at (for example, in a lesson)
- To be absent (from) – to be absent
- To be married – to be married
- To be single - to be single / not married
- To be lucky - to be lucky
- To be ready (for) - to be ready (for, for example, a lesson)
- To be afraid (of) – to be afraid
- To be interested (in) - to be interested in something
- To be ill / well - to be sick / to feel good
- To be angry (with) - to be angry, angry (at someone)
Let's conjugate together the expression to be married in affirmative, interrogative and negative sentences. What did you get?

The more you begin to appreciate and love your familiar native Russian language. It seems to us that in Russian there are no confusing tenses, no regular/irregular verbs, no articles. Everything is simple and clear. But this, of course, is not true. And the Russian language has its own complex rules and confusing definitions. In this article we will look at the slightly confusing construction there is/are, which is quite unusual because it is at the beginning of a sentence and is usually not translated in any way.
How and when to use there is/there are?
We use this construction when we need to say about location any item. That is, that something (someone) somewhere located. You need to immediately remember that we always put it at first offers. I think you have already guessed that we use there is when we are talking about one subject, and there are when we are talking about several.
We will literally translate the first sentence as follows: "There there is (is) book on the shelf". Of course, in Russian it sounds ugly, and no one talks like that in real life. But at the first stage it is important to understand meaning what we say .
This literal translation will help you speak correctly and, most importantly, understand the logic of this construction. But when you say this phrase many times and there is no need to translate it word for word, then you can move on to a beautiful literary translation: There are two books on the shelf.
Order of words in a sentence
with there is/are
Remember to put “there is/ there are” at the beginning when you talk about the location of something. This will help your interlocutor understand from the very beginning that we are talking about finding something somewhere. In such a sentence, each word is in its specific place. Let's look at the word order in a sentence.
| 1 place | 2nd place | 3rd place | 4th place |
| There | be (in the required form) | What (who) is | Where is |
| There | is | a cat | in the room |
| There | are | cats | in the street |
Negative form c there is/are
The negative form is formed by adding a particle not. It is used when you want to say that something no/wasn't/won't be anywhere. We can cut there is not = there isn't And there are not = there aren't.
Also with the construction there is/ there are the word is often used no (No). But abbreviations in such phrases are not allowed, because not is a particle that can be abbreviated, and no is a word that cannot be abbreviated.
How to ask questions with there is/are?
The construction of questions with this construction follows the standard rules of the English language. To ask a question, just move the words is/are to the beginning of the sentence, before the word there. Let's look at an example of how to turn an affirmative sentence into an interrogative one.
Statement
Question
A positive response will look like this.
At negative answer we add the particle not.
To reinforce this, let's look at another example.
How to ask questions using question words?
With the phrases there is/there are, you can also build sentences using question words. Here are some of them:
- what - what,
- which - which,
- why - why,
- how long - how long,
- when - when.
In such questions, we put these words first, and then the sentence is built as in a simple question.
There is/are in past and future tenses
 If you want to talk about something that was or will be somewhere, then for this it is enough to change form of words is/are (verb be). We will look at how this verb changes in great detail in the next article. For now, just remember that to change the tense using the construction there is/are, you need to change the verb.
If you want to talk about something that was or will be somewhere, then for this it is enough to change form of words is/are (verb be). We will look at how this verb changes in great detail in the next article. For now, just remember that to change the tense using the construction there is/are, you need to change the verb.
Since there is/there are is mainly used to say where is this or that object, then you can easily practice using this construction. Take a look around. What do you see? Where are the things you are used to? So, There is...
Verb be (be)
in the present tense has three forms: am, is, are:
am
used only with a pronounI
(I).
is
- with nounssingular.
are
- with nounsin plural
. Pronoun you in English it is always plural, although it can be translated into Russian as “you” or “you”.
Verb Declension Table to be in the present simple tense:
| I I | am | (not) (Not) |
fine. |
| He he/She she/It it | is | ||
| We we /You you /They they | are |
| I"m | ||
| abbreviations: | He's | |
| You"re |
I (am) a student. He (is) a student. Are you student. They are students.
I"m
not hungry, but I"m thirsty.
I'm not hungry, but I'm thirsty. (thirsty - adjective)
Kristy(she) is my niece.
Christy is my niece.
The weather is
n"t
very nice today.
The weather today is not very pleasant.
Kittens(they) are very funny.
Kittens are very funny.
My sister and I(we) are big fans of Lady Gaga.
My sister and I are big Lady Gaga fans.
"Game of Thrones"(it) is the most expensive TV show.
"Game of Thrones" is the most expensive TV series.
IN interrogative sentence am, is, are are brought before subject to. (In a declarative sentence, the verbs am, is, are come after the subject).
| Am | I | fine? | Yes, I am ./No, I"m not. |
| Is | he/she/it | Yes, he is ./No, he is n"t. | |
| Are | we/you/they | Yes, we are ./No, we are n"t. |
Are are you busy? - No, I"m not. I"m free now.
You're busy? - No. I'm free now.
Am I right? - No, you are
n"t. You are wrong.
I'm right? - No. You're wrong. (wrong - adjective)
Where is my rucksack? Your rucksack (it) is under the desk.
Where's my backpack? - Your backpack is under the table.
How old are your children (they)? - My son (he) is 8 and my daughter (she) is
6.
How old are your children? - My son is 8, and my daughter is 6.
The pie is so delicious. Is the recipe difficult?
This pie is so delicious. Is his recipe complicated?
Use of verbs am, is, are:
It is unusual for the Russian language to use the verb “to be” in the present tense, and is omitted in translation. And in English the verb to be is very important, since it is linking verb- connects different parts of speech (2 nouns, a noun and an adjective, a pronoun and a noun). Otherwise the sentence is incomplete in meaning: Our daughter is a biologist. - If translated literally, everything is fine - Our daughter is a biologist. But in English, without the verb is, this sentence is grammatically incorrect, since it is not clear how the daughter and the biologist are related. In order for a daughter to “become” a biologist, these two nouns must be connected with the verb is - Our daughter is a biologist. - Our daughter (is/is) a biologist.
Remember! Sentence in English cannot exist without a verb, therefore, if there is no semantic verb in a Russian sentence, then in this sentence in English it is necessary to use the linking verb “to be”, i.e. am, is or are:
Klaus comes from Germany.
Klaus is from Germany. (come is a semantic verb - the verb is is not needed)
Klaus is from Germany.
Klaus from Germany. (without is the sentence will remain without a verb)
You look beautiful!
You look great! (there is a verb look)
You are beautiful.
You are wonderful! (no semantic verb)
This dog seems very clever.
This dog seems very smart. (there is a verb seem)
This dog is very clever.
This dog is very smart. (no semantic verb)
Note! Some verbs of the Russian language into English are translated by adjectives with the verb to be: late (late), tired (tired), ill (sick), angry (angry), afraid (afraid), thirsty (thirsty).
I "m too tired to cook.
I'm too tired to cook.
Why are you always late?
Why are you always late?
I don't understand why she is angry with me.
I don't understand why she's angry with me.
My son and husband (they) are ill.
My son and husband got sick.
Little kids are often afraid of the dark.
Young children are often afraid of the dark.
The verb To Be is the most common verb in the English language.
Today we'll look at:
- how is it translated?
- forms of the verb To Be,
- how and where to use the verb To Be,
- rules and examples,
- verb To Be in all tenses.
If you are a complete beginner and just starting to learn English, first you need to understand what the verb to be is and in what cases it should be used. For a better understanding, I will give clear examples.
When to use the verb To Be - examples
When we need to indicate:
- profession, age, relationship,
- your location, citizenship,
- indicate the existence of something
- qualities of character,
- color and properties of objects,
- state of feeling or health,
- compare something/someone with something,
- Point at real process actions.
Examples:
I am a taxi driver, cook, director, translator, guy, citizen, etc..
She is my mother / sister / mother-in-law / friend / neighbor / good man/ in love / busy, etc.
He is good/bad/smart/funny/mean/cool/happy/sexy, etc.
It / It is real / rainy / healthy / red / easy, etc..
We are from Russia / in the park / at school / on the street / at work, etc..
They are better than.. / richer than.. / higher than.. faster than, etc..
More examples of what you can say using the verb To Be
What is this? Who is this? Where are you?
This is my home. It's Russia. Here's my friend.
The water is icy. The roads are good. Today is Friday.
Tomorrow is my birthday.
A wonderful day! It's complicated.
Are you ready? Is it dangerous?
Be careful.
Behave yourself.
Be happy.
Be a man!
She was right.
I'll be a lawyer.
We were great!
I'm reading /right now/
I'm driving / right now /
How to say all of the above in English, see the end of the article with translation.
Verb To Be NEVER not used with main verbs.
You can't say:
I am seeing. She is watching. He's going. They are working. We know.
I am seeing. She is watching. He's going. They are working. We know.
Verb To Be translation into Russian
The general meaning of the word To Be is - to be, is, be, appear, exist.
But when directly translated into Russian in the present tense, these words are usually omitted.
Examples of translation in the present tense:
1. I’m home = I’m at home. / I am at home/
2. She is a doctor = She is a doctor. /She is a doctor/
3. It’s in Russia = This is in Russia / This is or exists in Russia /
In the future tense, the verb has the form: will be and is translated as: I will, I will, I will.
In the past tense, the verb has the form: was/were and is translated as: was, were, was.
I was happy = I was happy.
They were right = They were right.
It was rainy last night = It was rainy last night.
To Be verb forms and abbreviations
The verb To Be is often shortened both in writing and in spoken language.
Remember these contractions and practice them.
I am = I'm
You are = You're
He is = He's
She is = She's
It is = It's
We are = We're
They are = They're
Examples of affirmative sentences of the verb To Be
I am a girl. I am a girl.
You are a boy. You are a boy.
He is clever. He is smart.
She is my sister. She is my sister.
It is a cat. It's a cat.
It's me. It's me.
We are friends. We are friends.
They are students. They are students.
Verb To Be - Negative Sentences
To say:
- I am NOT a taxi driver,
- I'm not at home,
- she is not from Russia,
- he is NOT evil,
- this is NOT true - i.e. in a negative form, then after the verb To Be we put a particle - Not -
See examples and abbreviations
I am not = I’m not
You are not = You're not
He is not = He’s not
She is not = She’s not
It is not = It’s not
We are not = We're not
They are not = They're not.
Verb To Be examples of negative sentences
I am not tired. I am not tired.
You are not a robot. You are not a robot.
He is not a driver. He's not a driver.
She is not rich. She's not rich.
It is not a dog. This is not a dog.
We are not ready. We're not ready.
They are not married. They are not married.
Verb To Be Interrogative sentences
To say:
- I am beautifull?
- He is good?
- They are from Russia?
- You are ready? — first we put the verb to be, then the pronoun.
Look at the examples:
Am I..? Are you..?
Is he..? Is she..? Is it..?
Are they..? Are we..?
Am I nice? I'm good?
Are you tall? You are tall?
Is he your dad? Is he your dad?
Is she pretty? She's beautiful?
Is it a cat? It's a cat?
Are we kids? Are we children?
Are they students? They are students?
The verb To Be is an Irregular verb.
This means that the verb changes its form not only depending on the gender of the noun, but also on what tense it is in.Check out the examples below.
Verb To Be in all tenses
Below are the conjugation tables for the verb To Be in three main tenses: this is the Simple group - present, past and future. This is quite enough for initial stage and up to the intermeddiate level.
Conjugation of the verb To Be in the present tense Present Simple
| Statement | Negation | Question |
| I am a doctor | I'm not a doctor | Am I a doctor? |
| You are a doctor | You are not a doctor | Are you a doctor? |
| He is a doctor | He is not a doctor | Is he a doctor? |
| She is a doctor | She is not a doctor | Is she a doctor? |
| It is a doctor | It is not a doctor | Is it a doctor? |
| We are doctors | We are not doctors | Are we doctors? |
| They are doctors | They are not doctors | Are they doctors? |
Conjugation of the verb To Be in the Past Simple
| Statement | Negation | Question |
| I was right | I wasn't right | Was I right? |
| You were right | You were not right | Are you right? |
| He was right | He wasn't right | Was he right? |
| She was right | She was not right | Was she right? |
| It was right | It was not right | Was it right? |
| We were right | We weren't right | Were we right? |
| They were right | They were not right | Were they right? |
Conjugation of the verb To Be in the future tense Future Simple
| Statement | Negation | Question |
| I will be in Moscow | I will not be in Moscow | Will I be in Moscow? |
| You will be in Moscow | You will not be in Moscow | Will you be in Moscow? |
| He will be in Moscow | He will not be in Moscow | Will he be in Moscow? |
| She will be in Moscow | She will not be in Moscow | Will she be in Moscow? |
| It will be in Moscow | It will not be in Moscow | Will it be in Moscow? |
| We will be in Moscow | We will not be in Moscow | Will we be in Moscow? |
| They will be in Moscow | They will not be in Moscow | Will they be in Moscow? |
Verb To Be to form action right now
In fact, the verb To Be participates in the formation of tenses of the Continuous group.
Examples:
I'm reading.
I'm reading (right now).
She is sleeping.
She's sleeping now.
We are going to the movies. We are going / now / to the cinema.
I was watching a video.
I watched the video.
They were walking down the street.
They were walking down the street.
And lastly,
Question words with the verb To Be
If a sentence uses question words, the question word comes first, then the verb to be.
When will you be home?
When will you be at home?
What is it?
What is this?
Who is tired?
Who's tired?
Now, consolidate the material you have covered.
Let's go back to our initial phrases that we say in life.
Check yourself if you translated them correctly.
1. I am a taxi driver, cook, director, translator, guy, citizen.
2. She is my mother, sister, mother-in-law, friend, neighbor, good person, in love, busy.
3. He is good, bad, smart, funny, stingy, funny, happy, sober, sexy.
4. It/It is real, rainy, healthy, red, easy.
5. We are from Russia, in the park, at school, on the street, at work.
6. They are better than.. / richer than.. / taller than.. faster than...
SEE HOW TO SAY THIS IN ENGLISH
1. I’m a taxi driver. I'm a cook. I'm a boss. I'm a translator. I'm a guy. I'm a citizen.
2. She is my mother. She is my sister. She is mother-in-law. She is my girlfriend. She is my neighbor. She is a nice person. She's in love. She is busy.
More examples using the verb To Be with translation into English
5. It’s a wonderful day! It's difficult.
6.Are you ready? Is it dangerous?
7. Be careful.
8. Be good.
9. Be happy.
10. Be a man!
11. She was right.
12. I’ll be a lawyer.
13. We were super!
14. I'm reading.
15. I'm driving.