The principle of operation of the air conditioner, its design features and troubleshooting methods
If there was a "grandfather Zhara", then in letters to him, children and adults would ask for only one thing - to give an air conditioner.
Today, many people cannot imagine their existence without this most useful device, and the vigorous spring drops heard near high-rise buildings with the advent of summer serve as another confirmation of this.
In this article, we will analyze the principle of operation of the air conditioner and the device equipment.
With all its diversity, air conditioners of different models are based on the same device - a heat pump. This ingenious mechanism allows heat transfer in the "unnatural" direction, that is, from a colder environment to a hotter one.
Let's show how it works schematically:
- Let's take two containers with a certain medium, and the temperature in the 1st container is lower than in the 2nd. Let's place a vessel with gas in the 1st container and wait until the temperatures of the gas and the medium are equal.
- Let us move the gas into the 2nd container and compress it so that its temperature (recall that gases heat up during compression) is higher than the temperature of the medium in this container. Due to the temperature difference, heat exchange will begin, that is, the gas will begin to give off thermal energy to the environment of the 2nd tank.
- Again we move the gas to the 1st container, while returning it to its original volume. As the gas expands, it will cool down, and since part of the internal energy was lost by it in the previous stage, its temperature will be lower than it was at the beginning. That is, the gas after expansion will be colder than the medium in the 1st container. Heat exchange will again take place, only in the medium-gas direction. After balancing the temperatures, we will again transfer the gas to the 2nd container, not forgetting to compress it at the same time. So the heat will gradually be “pumped” from the cold substance to the hot one.
Heat pumps work not only under the guise of air conditioners, but also refrigerators, dehumidifiers, geothermal heating systems, etc. The gas used in them is called a refrigerant, freon is usually used in this capacity.

The device and principle of operation of the air conditioner
The refrigerant circulates through a closed pipe circuit consisting of two parts: a condenser, in which the gas is compressed to a liquid state, and an evaporator, in which the refrigerant evaporates, turning back into a gas and expanding in volume.
From the evaporator to the condenser, the gas enters with the help of a compressor (it also compresses). From the condenser, the refrigerant gradually seeps back into the evaporator through a long thin tube twisted into a cylindrical spiral (it is called a capillary, throttle or expansion valve).
Varieties of air conditioners
 Today, in addition to conventional air conditioners that periodically turn on and off, so-called inverter devices are produced.
Today, in addition to conventional air conditioners that periodically turn on and off, so-called inverter devices are produced.
An inverter is an electronic unit that allows you to arbitrarily change the frequency of the electric current. In this case, the compressor power will also change accordingly.
Thus, the inverter air conditioner does not need to be turned off - it works constantly, choosing the optimal cooling capacity.
The temperature value in the room remains fixed, and the device lasts longer than its non-inverter counterparts (start-up moments greatly reduce the life of power generating sets).
Also, air conditioners can be:
- recycling- they simply drive the air of the room through themselves.
- With the possibility of mixing outside air: these devices are more expensive than recirculating ones, but the air in the room where they are installed not only becomes cool, but also remains fresh.
According to the way the units are arranged, air conditioners are divided into two types: monoblocks and split systems.
 Most air conditioners have a heating function, but not everyone knows. We will talk about this in the article.
Most air conditioners have a heating function, but not everyone knows. We will talk about this in the article.
Consider the types and arrangement of a boiler for heating water.
And in this topic an overview of the heating schemes of a two-story house is presented. Vertical and horizontal options.
Monoblocks
All the "stuffing" of such a device is in one case, so that the product has a low cost. There are the following types of monoblocks:
- Window: installed in a window or wall opening so that the condenser is outside, and the evaporator is inside the room.
- Roof: installed in the same way, only in the roof.
- Mobile: the entire device stands on the floor inside the room, and the air blown by the hot condenser is discharged through the duct to the street.

mobile air conditioner
For a price gain, the owner of a monoblock has to endure the noise from the compressor and put up with heat leaks in winter through the device case (the latter is relevant for window and roof models).
Split systems
The device consists of two parts, one of which is placed indoors, and the other is outdoors. If there is one outdoor unit and several indoor units, the device is called a multi-split system. Such air conditioners are the most popular today, so we will consider their work in more detail.
System operation
Consider how an air conditioner works. Let's start with the principle of operation of a split air conditioner system. So, the split system consists of such components.
Outdoor unit air conditioner
There is a condenser with a fan blowing it and a compressor. Thus, the noisiest nodes were on the street, which is the main advantage of split systems.
Consider the principle of operation of the air conditioner compressor. The compressor compresses the refrigerant to a pressure of 20 - 25 atm, as a result of which its temperature rises to 90 degrees. Reciprocating compressors are the cheapest, but their reliability leaves much to be desired, especially if it's cold outside. More expensive scroll compressors do not have this disadvantage.
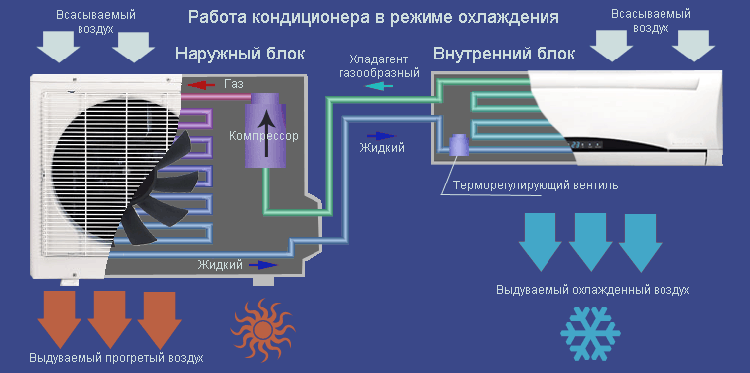
The principle of operation of a split system for cooling
Models in which the outdoor unit fan rotates at a constant speed only operate effectively in a narrow range of outdoor temperatures. In more "advanced" air conditioners, the fan speed is smoothly or stepwise controlled depending on the temperature.
Freon is gradually squeezed through the capillary into the tube leading to the second part of the device. It is called…
indoor unit
 An evaporator is placed here, which is also blown by a fan. In addition, there is a control board, an air filter and a condensate collection tray (discharged through a drain hose).
An evaporator is placed here, which is also blown by a fan. In addition, there is a control board, an air filter and a condensate collection tray (discharged through a drain hose).
Freon pressure in the evaporator is 4 - 5 atm, while it cools down to a temperature of less than 10 degrees.
According to the type of indoor unit (WB), split air conditioners are divided into the following types:
- Wall mounted: WB is placed on the wall in its upper part. The cooled air is supplied directly to the room.
- Cassette: are installed in the center of the ceiling with the expectation that all communications will be hidden by the suspended ceiling. The WB itself has the same dimensions as a standard ceiling tile - 60x60 cm. Powerful models have a double size - 120x60 cm. Cooled air is also supplied directly to the room, but, unlike the wall version, in four directions at once. Thanks to this, it is possible to effectively cool a room with a much larger area.
- Channel: The duct-type WB is completely hidden behind the false ceiling, and the cooled air is supplied through a network of air ducts. Thus, with the help of one WB, it is possible to cool the air in several rooms.
![]()
The device of the indoor unit of the air conditioner
Most modern air conditioners can operate in two modes:
- Cold operation of the air conditioner: this is the normal mode in which the condenser is placed outside and the evaporator is placed in the room.
- The operation of the air conditioner for heat.
In air conditioners capable of operating in heating mode, the external and internal parts of the circuit can change roles: the internal becomes a condenser, and the external becomes an evaporator. To do this, a jumper and a 4-way valve are added to the circuit, which directs the refrigerant to one or another line.
A feature of heater air conditioners is that their thermal power is 3-4 times higher than the consumed electrical power, while for conventional electric heaters both of these parameters have equal values.
Possible system malfunctions
In order not to harm the air conditioner, you need to know what it can break. Here are the most common reasons:
Clogged air filter
 This is evidenced by a significant weakening of the air flow blowing from the air conditioner.
This is evidenced by a significant weakening of the air flow blowing from the air conditioner.
With a certain frequency, the filter must be washed with running water, as a result of which its working qualities will be restored.
If even after cleaning the filter the situation has not changed, inspect the evaporator: perhaps a lot of dust has also accumulated on it.
Undesirable organics started up in the indoor unit
The owner immediately recognizes this by an unpleasant smell. Microbes settle and multiply on the evaporator, where life-giving condensate is formed. The radiator should be treated with a special disinfectant.
Clogged condensate drain
 In this case, water will flow from the indoor unit. Usually clogging is caused by dust.
In this case, water will flow from the indoor unit. Usually clogging is caused by dust.
It is contained in the air driven through the air conditioner, and part of it settles on the evaporator wet from condensate.
Then, together with moisture, it flows into the outlet tube and clogs it. After cleaning the system, the water will leave along the project path.
The compressor has failed
Some users try to heat up the air conditioner even when the outside temperature drops below +5 degrees, although its compressor is not designed for this (this does not apply to some special models). As a result, the unit fails. In order for the device to be used even in cold weather, a compressor heating system must be installed.
water hammer
The reason for the occurrence of this phenomenon is the flow of refrigerant into the compressor in liquid form - before it turns into a gaseous state in the evaporator. In this case, the latter may be damaged.Freon does not have time to evaporate due to hypothermia, which can be caused by two reasons: starting the device in frosty weather and clogging the filters with dust (the evaporator is blown worse by warm air from the room).






